| 來源 |
I created this work entirely by myself. Sources Penguin historical atlas of Greece, Historical Atlas — William R. Shepherd.
- For Mauryan-Seleucid boundaries extent:
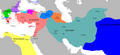
" Seleukus, one of Alexander's generals, had made himself king of western and central Asia. But in 305 B.C. Chandragupta, after a successful campaign, forced him not only to give up all thought of conquest in India but also to cede the provinces of Parapamisadai, Aria, Arachosia, and probably Gedrosia . Thus the Hindu Kush mountains became the frontier of the first Indian Empire. Its capital was Pataliputra (now Patna). Chandragupta died in 297 B.C. and was succeeded by his son Bindusura (272 B.C.) and his grandson, the renowned Asoka (272-232). Asoka's Empire extended in the north-west to the Hindu Kush, and included most of the territory now called Afghanistan, the greater part of Baluchistan, and all Sindh. Northwards his dominions stretched to the foot of the Himalayas and seem to have comprised the districts round Srinagar (which was built by him) and the territory round Lalita Patan in Nepal, two and a half miles south-east of Kathmandu (also built by him). The whole of Bengal acknowledged his sway, and the kingdom of Kalinga (i.e., the strip of country extending along the coast of the Bay of Bengal from the Mahanadi to the Godaveri) was subjugated in 261 B.C. The Dekkan had already been conquered either by Chandragupta or by Bindusura. The Andhra kingdom, between the Godaveri and the Kistna, was administered by its own raja, but seems to have been a protected state. The southern frontier of the empire must have coincided closely with the 13th degree of northern latitude. The southern Tamil kingdoms of Chola, Pandya, Satiya, and Chera remained independent."
- Historical atlas of India by Charles Joppen[1]
Pg.75 : Chandragupta Maurya, and the four satrapies of Aria, Arachosia, Gedrosia, and the Paropanisadai were ceded to him by Seleukos Nikator about B.C. 305. The Maurya frontier was thus extended as far as the Hindû Kush Mountains, and the greater part of the countries now called Afghanistan, Balûchistan and Makran, with the North-Western Frontier Province, became incorporated in the Indian Empire. That empire included the famous strongholds of Kabul, Zabul, Kandahar, and Herat, and so possessed the scientific frontier' for which Anglo-Indian statesmen have long sighed in vain.
- Asoka, the Buddhist emperor of India by Smith, Vincent Arthur [2]
Pg.105 : Net result of the expedition, however, clearly indicate that Seleucus met with a miserable failure. For he had not only to finally abandon the idea of reconquering the Panjab, but had to buy peace by ceding Paropanisadai, Arachosia, and Aria, three rich provinces with the cities now known as Kabul, Kandähär and Herät respectively as their capitals, and also Gedrosia (Baluchistan), or at least a part of it. The victorious Maurya king probably married the daughter of his Greek rival, and made a present of five hundred elephants to his royl father-in-law.
- Ancient India by R. C. Majumdar[3]
Pg. 170 : By 311 B.C. or somewhat later the Indus had become the frontier of the Magadhan Empire. Further westward expansion was largely the outcome of the successful military encounter with Seleucus Nicator (Seleukos Nikator), founder of the Seleucid dynasty and inheritor of Alexander's eastern empire from northern Syria to India Between 305 and 302 B.C. Seleucus ceded the satrapies of Gedrosia. Arachosia, Paropamisadai, and probably Aria , gave his adversary a Greek princess in marriage, and obtained in return 500 war elephants and permanent peace and friendship on his eastern frontier. About this time, perhaps earlier, western Gandhara and areas north to the Hindu Kush, Abhisara, and probably Kasmira were also annexed to the Mauryan dominions.
- Historical Atlas of India by Joseph E. Schwartzberg [4]
Pg.33 : The ancient historians Justin, Appian, and Strabo preserve the three main terms of what I will call the Treaty of the Indus: (i) Seleucus transferred to Chandragupta's kingdom the easternmost satrapies of his empire, certainly Gandhara, Parapamisadae, and the eastern parts of Gedrosia, and possibly also Arachosia and Aria as far as Herat. (ii) Chandragupta gave Seleucus 500 Indian war elephants. (iii) The two kings were joined by some kind of marriage alliance (ἐπιγαμία οι κῆδος); most likely Chandragupta wed a female relative of Seleucus.
- The Land of the Elephant Kings by Paul J Kosmin [5]
Pg. 15 : Towards the north-west, his empire marched with that of the Syrian monarch, Antiochos [R.E. II], and hence extended up to Persia and Syria which were held by Antiochos, while it is also known how Asoka's grandfather, Chandragupta, had wrested from Selukos the provinces of Aria, Arachosia, Paropanisadai and Gedrosia, which descended to Asoka as his inheritance. Lastly, the extent of his empire is also indicated by his own mention in the Edicts (Rock Edict II, V, and XIII] of the peoples on its borders In the south, these are mentioned as the Cholas, Pandyas, the Satiyaputra and Keralaputra, who were all within his sphere of influence Towards the north-west, his empire marched with that of the Syrian monarch, Antiochos [Rock Edict II], and hence extended up to Persia and Syria which were held by Antiochos, while it is also known how Asoka's grandfather, Chandragupta, had wrested from Selukos the provinces of Aria, Arachosia, Paropanisadai and Gedrosia, which descended to Asoka as his inheritance .
- Asoka by Radhakumud Mookerji[6]
|