磁鼓存储器
外观
(重定向自磁鼓)
| 计算机存储器类型 |
|---|
| 易失性存储器 |
| RAM |
| 发展中 |
| 历史上 |
| 非易失性存储器 |
| ROM |
| 非揮發性隨機存取記憶體 |
| 早期非易失性随机存取存储器 |
| 磁式 |
| 光學式 |
| 发展中 |
| 历史上 |
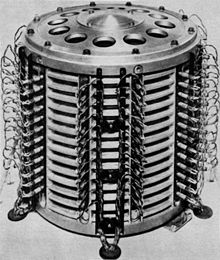
磁鼓記憶體(英語:Drum memory)是一种依靠磁介质的資料儲存裝置,為20世纪50年代和60年代计算机所用記憶體的早期形式,由Gustav Tauschek于1932年在奥地利发明。磁鼓为这套机制的主要工作储存單元,透過穿孔纸带或者打孔卡加载、取出資料。当时许多计算机采用了这种磁鼓記憶體,以至于它们常常被叫做“鼓机”(drum machines)。不过不久之后,磁芯記憶體等其他技术取代了磁鼓器成为了主要的儲存媒体,直到最后半导体記憶體进入了儲存媒体的领域。
外部链接
[编辑]- The Story of Mel (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) – the classic story about one programmer's drum machine hand-coding antics: Mel Kaye.
- Librascope LGP-30 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) – The drum memory computer referenced in the above story, also referenced on Librascope LGP-30.
- Librascope RPC-4000 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) – Another drum memory computer referenced in the above story
- Oral history interview with Dean Babcock (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆). Charles Babbage Institute, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. Babcock discusses various ERA projects including Project Lime; magnetic drum designs and capabilities; the work of Sidney Rubens and William Field on magnetic drums; and ERA's interaction with the Navy during the Korean War.
