隱藻門
外观
(重定向自隐藻)
| 隐藻总纲 | |
|---|---|
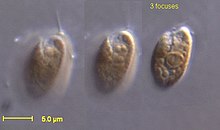
| |
| Rhodomonas salina | |
| 科学分类 | |
| 域: | 真核域 Eukaryota |
| 演化支: | 多貌生物 Diaphoretickes |
| 演化支: | CAM |
| 演化支: | 原始质体生物 Archaeplastida |
| 门: | 隐藻门 Cryptophyta |
| 总纲: | 隐藻总纲 Cryptomonada Margulis & Schwartz 1998 ex Cavalier-Smith 2004 em. Cavalier-Smith 2015[1] |
| 纲和目 | |
| 異名 | |
| |
隐藻门是一大类的藻类,[2]大都具有色素体,淡水中常见。细胞大小约为10-50微米,形状扁平,有两个稍微不等长的鞭毛。一个著名特征是有红藻寄生于其细胞中,形成一种内共生关系,并把藻胆素带给宿主。
原本一般认为其与定鞭藻門关系更为密切,但2015年牛津大学卡瓦利埃 - 史密斯等人的研究[3]及2016年加拿大不列颠哥伦比亚大学帕特里克 · 基林等人的研究[4]显示其实际上是原始色素體生物的一部分,至于其与其他植物的系统发生关系则仍不明确。[3][4]
下属分类
[编辑]本门包括以下纲:
- 隐藻纲 Cryptophyceae
- Goniomonadea [5]
- Goniomonadophyceae
- Goniomonadales
- Katablepharidophyceae
- Leucocryptea [6]
- Kathablepharida
- Palpitea
- Palpitida
- Telonemea
- Telonemida
参考文献
[编辑]- ^ de Reviers, B. Biologia e Filogenia das Algas [Biology and Phylogeny of Algae]. Porto Alegre: Artmed Editora. 2006: 15. ISBN 978-8-5363-1510-2 (西班牙语).
- ^ Khan H, Archibald JM. Lateral transfer of introns in the cryptophyte plastid genome. Nucleic Acids Res. May 2008, 36 (9): 3043–53 [2012-09-04]. PMC 2396441
 . PMID 18397952. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn095. (原始内容存档于2020-04-13).
. PMID 18397952. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn095. (原始内容存档于2020-04-13).
- ^ 3.0 3.1 Cavalier-Smith, Thomas; Chao, Ema E.; Lewis, Rhodri. Multiple origins of Heliozoa from flagellate ancestors: New cryptist subphylum Corbihelia, superclass Corbistoma, and monophyly of Haptista, Cryptista, Hacrobia and Chromista. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 2015-12, 93: 331–362 [2018-11-24]. ISSN 1055-7903. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2015.07.004. (原始内容存档于2021-04-03).
- ^ 4.0 4.1 Burki, Fabien; Kaplan, Maia; Tikhonenkov, Denis V.; Zlatogursky, Vasily; Minh, Bui Quang; Radaykina, Liudmila V.; Smirnov, Alexey; Mylnikov, Alexander P.; Keeling, Patrick J. Untangling the early diversification of eukaryotes: a phylogenomic study of the evolutionary origins of Centrohelida, Haptophyta and Cryptista. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2016-01-27, 283 (1823): 20152802 [2018-11-24]. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 4795036
 . PMID 26817772. doi:10.1098/rspb.2015.2802. (原始内容存档于2018-11-06) (英语).
. PMID 26817772. doi:10.1098/rspb.2015.2802. (原始内容存档于2018-11-06) (英语).
- ^ Cavalier-Smith, T. (1993). Kingdom Protozoa and its 18 phyla. Microbiological Reviews. 57(4): 953-994.
- ^ Cavalier-Smith, T.; Chao, E. (2004). Protalveolate phylogeny and systematics and the origins of Sporozoa and dinoflagellates (phylum Myzozoa nom. nov.). European Journal of Protistology. 40(3): 185-212.
