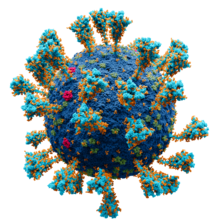
刺突醣蛋白 (spike (S) glycoprotein)[ 2] 刺突蛋白 [ 3] 棘蛋白 、S蛋白 ,旧名 E2 [ 4] 冠状病毒 中最大的一种结构蛋白 [ 5] 病毒进入 宿主细胞 ,在病毒感染期间介导受体识别、细胞附着和融合[ 6]
由于刺突蛋白可結合成蛋白三聚體 ,此時可以看到病毒体 表面有突出的大结构,称为“刺突”[ 4] [ 5] [ 7] [ 8]
刺突糖蛋白 可以与細胞表面受體 相互作用,然后病毒膜和细胞膜就會融合,最終导致病毒进入宿主细胞 免疫原性 。人們從嚴重急性呼吸系統綜合症 和2019冠状病毒病疫情 康复的患者中发现了專門针对刺突糖蛋白的抗体 [ 9]
^ Solodovnikov, Alexey; Arkhipova, Valeria. Достоверно красиво: как мы сделали 3D-модель SARS-CoV-2 [Truly beautiful: how we made the SARS-CoV-2 3D model] . N+1 . 29 July 2021 [30 July 2021] . (原始内容 存档于30 July 2021) (俄语) . ^ Shen S, Tan T H P, Tan Y J. Expression, glycosylation, and modification of the spike (S) glycoprotein of SARS CoV[J]. Glycovirology Protocols, 2007: 127-135.
^ Deng, X.; Baker, S.C. Coronaviruses: Molecular Biology (Coronaviridae). Encyclopedia of Virology. 2021: 198–207. ISBN 9780128145166doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-814515-9.02550-9 ^ 4.0 4.1 Masters, Paul S. The Molecular Biology of Coronaviruses . Advances in Virus Research. 2006, 66 : 193–292. ISBN 9780120398690PMC 7112330 PMID 16877062 doi:10.1016/S0065-3527(06)66005-3 ^ 5.0 5.1 Wang, Yuhang; Grunewald, Matthew; Perlman, Stanley. Coronaviruses: An Updated Overview of Their Replication and Pathogenesis. Coronaviruses. Methods in Molecular Biology 2203 . 2020: 1–29. ISBN 978-1-0716-0899-9PMC 7682345 PMID 32833200 doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-0900-2_1 ^ Huang, Y., Yang, C., Xu, Xf. et al. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol Sin 41, 1141–1149 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-0485-4
^ Zhu, Chaogeng; He, Guiyun; Yin, Qinqin; Zeng, Lin; Ye, Xiangli; Shi, Yongzhong; Xu, Wei. Molecular biology of the SARs‐CoV‐2 spike protein: A review of current knowledge . Journal of Medical Virology. 14 June 2021, 93 (10): 5729–5741. PMC 8427004 PMID 34125455 doi:10.1002/jmv.27132 ^ 存档副本 . [2022-06-03 ] . (原始内容 存档于2022-02-12). ^ V’kovski, Philip; Kratzel, Annika; Steiner, Silvio; Stalder, Hanspeter; Thiel, Volker. Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2 . Nature Reviews Microbiology. March 2021, 19 (3): 155–170. PMC 7592455 PMID 33116300 doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6
 . PMID 16877062. doi:10.1016/S0065-3527(06)66005-3.
. PMID 16877062. doi:10.1016/S0065-3527(06)66005-3.
 . PMID 32833200. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-0900-2_1.
. PMID 32833200. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-0900-2_1.
 . PMID 34125455. doi:10.1002/jmv.27132.
. PMID 34125455. doi:10.1002/jmv.27132.
 . PMID 33116300. doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6.
. PMID 33116300. doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6.
